At the Vein Institute of New Jersey, we often encounter patients who are curious about the best treatments for their vein conditions. Recently, Varithena is being used more often by doctor groups across the county.
To help you understand your options, let's compare Varithena with the more traditional Sclerotherapy and Ablation treatments, focusing on their uses, effectiveness, and what conditions they are best suited for.
Varithena: The New Trend in Varicose Vein Treatment
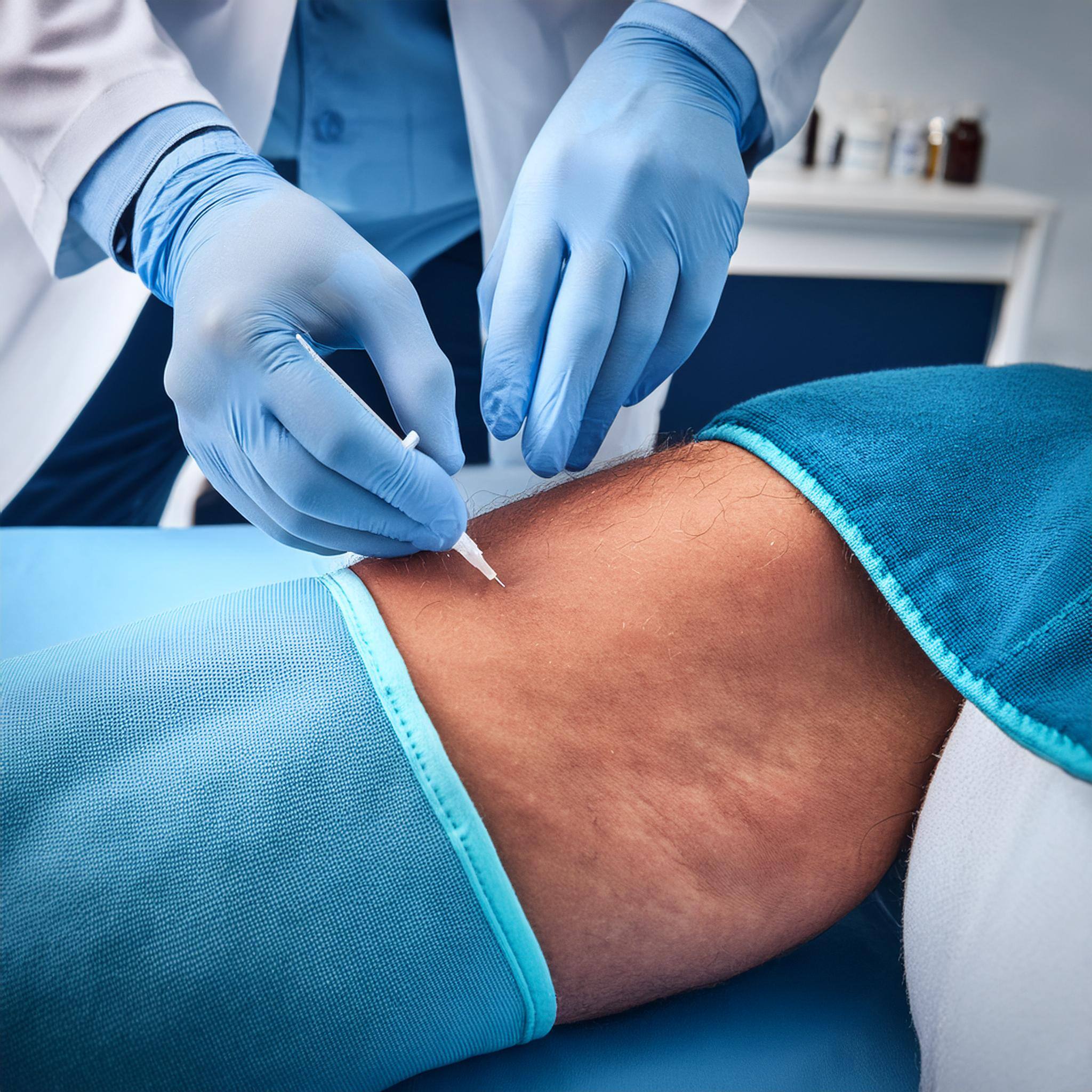
Varithena is a minimally invasive treatment specifically designed for varicose veins. It involves the injection of a microfoam that fills and collapses the affected vein, redirecting blood flow to healthier veins. Here are some key points about Varithena:
- Effectiveness: Varithena is highly effective in treating varicose veins, particularly in the great saphenous vein and its tributaries.
- Procedure: The procedure is quick, usually taking less than an hour, and is performed in-office with minimal discomfort.
- Recovery: Patients can resume most activities immediately with minimal downtime, though will be required to wear a compression stocking until the post-op visit occurs.
- Results: Most patients notice significant improvement in the appearance of their varicose veins and symptoms like pain and swelling.
Sclerotherapy: The Go-To for Spider Veins
Sclerotherapy is a widely used treatment for spider veins and smaller varicose veins. It involves injecting a solution directly into the vein, causing it to collapse and fade over time. Here's what you need to know about Sclerotherapy:
- Effectiveness: Sclerotherapy is particularly effective for spider veins and smaller varicose veins.
- Procedure: This in-office procedure takes about 30 minutes and may require multiple sessions depending on the extent of the vein issue.
- Recovery: Patients can return to normal activities immediately, though should avoid exposure to sunlight for one week.
- Results: Results become visible within a few weeks, with treated veins gradually fading.
Ablation: Another Option for Varicose Veins
Ablation treatments, including endovenous laser ablation (EVLA) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA), are also popular for treating varicose veins. These methods use heat to close off the problematic vein. Here's a quick overview:
- Effectiveness: Ablation is effective for larger varicose veins and often used when veins are deeper or more severe.
- Procedure: Performed under local anesthesia, the procedure involves inserting a catheter into the vein and using laser or radiofrequency energy to seal it.
- Recovery: Most patients can resume regular activities within a day or two, but strenuous activities should be avoided for a week or two.
- Results: Immediate improvement in symptoms is common, with cosmetic results becoming apparent over several weeks.
Comparing the Treatments
- Target Veins: Varithena is mainly for larger varicose veins, while Sclerotherapy is best for spider veins and smaller varicose veins. Ablation is used for larger, deeper varicose veins.
- Procedure Time: Varithena and Sclerotherapy are quicker procedures, often completed within 30-45 minutes, while Ablation may take a bit longer.
- Recovery Time: All three treatments offer minimal downtime, but Ablation might require slightly longer recovery.
- Results: All treatments are effective, but the choice depends on the size, location and type of veins being treated. Varithena and Ablation often provide faster symptom relief, while Sclerotherapy is ideal for cosmetic improvement of smaller veins.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The best treatment for you depends on your specific condition, the size and location of your veins, and your personal preferences. At the Vein Institute of New Jersey, our specialists will work with you to determine the most suitable option, ensuring optimal results and a smooth recovery.
If you have any questions or want to schedule a consultation, please contact us. We’re here to help you achieve healthier, more beautiful legs!







.jpg?width=944&name=Castle-Connolly-Top-Doctors-Emblem-Large%20(4).jpg)