Blood clots are the body’s natural response to injury, helping to prevent excessive bleeding. However, when they form inappropriately—especially in the deep veins—they can pose serious health risks. Knowing when to be concerned about a blood clot can mean the difference between prompt treatment and a life-threatening emergency.
Here’s what you need to know.
Understanding Blood Clots
A blood clot, or thrombus, is a gel-like clump of blood. While clots are helpful in stopping bleeding, they become dangerous when they form in veins without injury or don't dissolve on their own. A common and serious condition is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), which occurs when a clot forms in the deep veins, typically in the legs.
If part of the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism (PE), a potentially fatal condition.
Signs and Symptoms of a Blood Clot
Be alert to the following signs, especially if they occur in just one leg:
- Swelling (often sudden and isolated)
- Pain or tenderness in the calf or thigh, often described as cramping
- Warmth over the affected area
- Discoloration (redness or a bluish tone)
If the clot has moved to your lungs (pulmonary embolism), symptoms may include:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing
- A rapid heart rate
- Coughing, sometimes with bloody mucus
These symptoms require emergency medical attention.
When Should You Be Concerned?
You should be especially alert if you:
- Recently had surgery or were on bed rest
- Have taken long trips without movement (like plane or car travel)
- Use hormonal birth control or hormone replacement therapy
- Have a family history of clotting disorders
- Are pregnant or recently postpartum
- Have cancer or are undergoing cancer treatment
- Smoke or are overweight
Even if symptoms seem minor, it’s always better to err on the side of caution. Delaying care can increase the risk of complications.
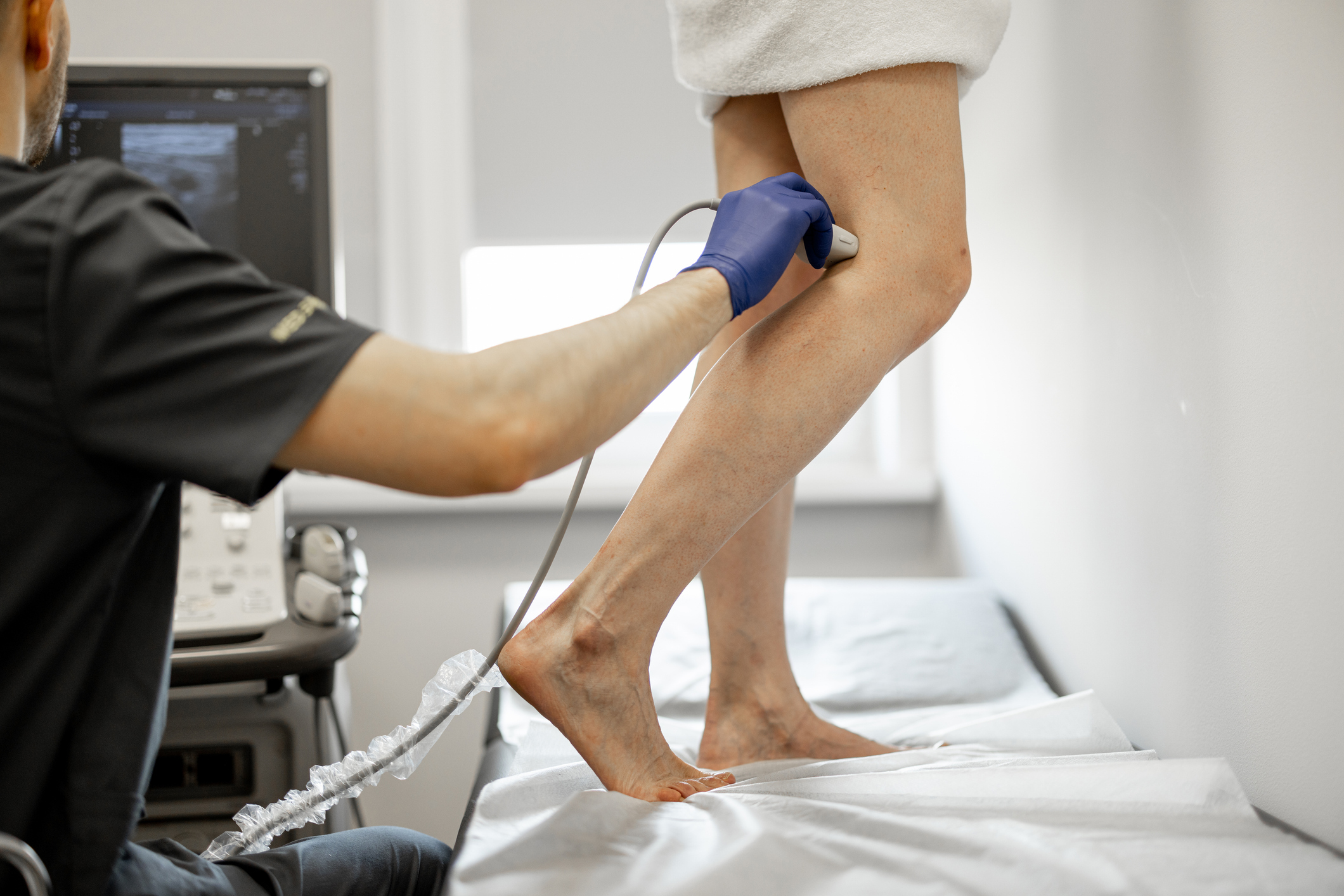
How Are Blood Clots Diagnosed?
At the Vein Institute of New Jersey, we use vascular ultrasound to quickly and safely assess for clots in the veins. This noninvasive imaging technique helps us see the blood flow in your veins and locate any blockages.
What Happens if a Blood Clot is Found?
If a clot is diagnosed, your doctor may recommend:
- Anticoagulant (blood thinning) medications to prevent further clotting
- Compression stockings to support blood flow
- Minimally invasive procedures in some cases, such as thrombolysis
Our team of board-certified vascular specialists is trained to assess each case individually and recommend the best course of treatment.
Preventing Future Clots
Simple lifestyle changes can reduce your risk:
- Stay active and move regularly, especially during travel
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid smoking
- Follow your doctor’s advice if you're at higher risk
Concerned About a Blood Clot? Don’t Wait.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of a blood clot or have concerns about your vein health, contact the Vein Institute of New Jersey. We offer same-day evaluations and in-office vascular imaging to provide quick answers and peace of mind.
Your legs carry you through life—don’t ignore their warning signs.







.jpg?width=944&name=Castle-Connolly-Top-Doctors-Emblem-Large%20(4).jpg)